A Guideline to Optimize Nutrient Requirements of Cattle
Introduction

Cattle farming is crucial in fulfilling the world’s demand for meat and dairy products. Understanding your herd’s nutrient requirements as a cattle owner or farmer is essential for their general health, growth, and production. In this post, we will look at the basic nutrients that cattle require for optimal growth and give you useful information on how to optimize their nutrition.
Table of Contents
Here are some of the most important nutrient requirements of cattle:
1. Water Requirements of Cattle: The Essential Element of the Cattle Diet
For cattle, water is the most important element. It’s necessary for hydration, digestion, food absorption, and temperature regulation. Cattle should have always access to clean and fresh water. Adequate water consumption promotes rumen function and general health.
The amount of water consumed by cattle is influenced by various factors, including dry matter consumption, environmental conditions, and physiological status. Here are some water consumption guidelines based on dry matter intake:

General Rule: As a general thumb rule, animals kept under cool conditions (temperature below 20 °C) usually need 4-5 liters of water for every kg of dry matter eaten. But once the temperature rises above 30°C, the amount of water requirements increases up to 10-12 liters per kg dry matter.
Example Calculation of The Water Requirements of Cattle: To estimate the water consumption based on dry matter intake basis, let’s consider a 300 kg beef cow consuming 7.6 kg of dry matter in a day at a cool temperature. Following the general rule, the cow would require around (7.6 x 4) = 30.4 Liter to (7.6 x 5) = 38 Liter (approximately) of water on that day.
Environmental Factors: It should be noted that environmental factors can have an impact on water requirements. Cattle may need to drink more water in hot and humid conditions to be hydrated and maintain their body temperature.
Considerations: Certain physiological conditions, such as lactation or high-performance activities, can increase cattle’s water consumption. To fulfill these increasing demands, it is crucial to ensure constant access to clean and fresh water.
Water Quality: It is also important to ensure good water quality. To maintain optimal cattle health and performance, water supplies should be free of pollutants and evaluated regularly.
2. Energy: A Source of Growth and Performance
Energy is an essential component of cattle diets because it fuels growth, reproduction, and physical activity. Cattle receive energy from their diet, which contains carbs, lipids, and proteins. To address their energy requirements, high-quality forages, cereals, and supplemental feeds are often employed. To avoid metabolic problems and maintain a healthy body condition, it is critical to balance energy consumption with other nutrients.
3. Protein: Muscle Development Building Blocks
Protein is required for cattle for muscle development, tissue repair, and general growth. It is made up of amino acids, which serve as the building blocks for many biological activities. Cattle require a diet that includes both non-protein nitrogen (NPN) and true protein sources. Protein supplements, together with high-quality forages like legumes, can guarantee enough crude protein consumption for peak performance.
4. Mineral Requirements of Cattle
Minerals are essential for cattle’s general health and well-being. These essential components are necessary for a variety of physiological functions, including bone growth, enzyme activity, immunological support, and reproduction. The following are some essential minerals requirements for cattle:

Macro Mineral Requirements of Cattle
Here are some of the most essential macro minerals for cattle:
- Calcium (Ca): Calcium is essential for bone growth, muscular function, and nerve transmission. It is especially critical for growing calves, breastfeeding cows, and milk production.
- Phosphorus (P): Phosphorus, along with calcium, promotes bone and tooth formation, energy metabolism, and overall cell function. It is essential for optimum growth and reproduction.
- Magnesium (Mg): Magnesium is essential for enzyme activity, nerve function, and energy metabolism. It is essential for preventing grass tetany and maintaining normal muscular function.
- Potassium (K): Potassium aids in the maintenance of fluid equilibrium, neuron function, and muscular contractions. It is required for appropriate heart function as well as overall cell health.
- Sodium (Na): Sodium is required for fluid balance, acid-base homeostasis, and nerve impulse transmission. Cattle get sodium from their feed and drinking water. Salt is the main source of sodium supply in cattle diets.
- Sulfur (S): Sulfur is required for protein synthesis, hoof health, and immunological function in general. It contains amino acids and vitamins.
Trace Mineral (Micro Mineral) Requirements of Cattle:
In addition to macro minerals, cattle also require trace minerals or micro minerals in their diet. Cattle require trace minerals in smaller amounts compared to macro minerals. These micronutrients are required for a variety of physiological functions, including overall health, reproduction, immunological function, and growth.
Here are some of the most important trace minerals for cattle:
Copper (Cu), Zinc (Zn), Manganese (Mn), Selenium (Se), Iron (Fe), Iodine (I), Chromium (Cr), Cobalt (Co), and Molybdenum (Mo) are among them. These trace minerals or micro minerals are required for enzyme function, immune system support, and reproductive function.
5. Vitamin Requirements of Cattle
Vitamins are essential for cattle’s overall health and fertility. These important nutrients are required for a variety of physiological processes such as immune function assistance, reproduction, growth, and metabolism. Here are some of the most important vitamins requirements for cattle:

- Vitamin A: Vitamin A is required for cattle vision, immune system functioning, and fertility. It’s common in green forages like new pastures or high-quality hay.
- Vitamin D: Vitamin D helps calcium and phosphorus absorption, resulting in bone health and growth. Cattle can receive vitamin D from the sun or from dietary sources such as fortified diets.
- Vitamin E: Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that protects cells from damage and promotes immune system function. Fresh forages, grains, and oilseed meals all contain it.
- Vitamin K: Vitamin K is required for the proper blood coagulation process and bone development in cattle. It is produced by rumen microorganisms and is also found in green forages.
- B-vitamins: The B-vitamin complex, which includes thiamin (B1), riboflavin (B2), niacin (B3), pantothenic acid (B5), pyridoxine (B6), cobalamin (B12), and folic acid, is essential for energy metabolism and overall health. These vitamins are found in a variety of feeds and are produced by rumen microorganisms.
- Vitamin C: While cattle can synthesize vitamin C internally, under certain stressful conditions, their demand may increase. Vitamin C is found in fresh forages and certain concentrates.
6. Fiber: Improves Digestion and Gut Health
Fiber is an important component of cattle diets, particularly for ruminants. It improves optimum digestion by assisting in the fermentation process in the rumen. Forages such as grasses and hay give cattle the fiber they needed. Adequate fiber consumption promotes rumen health, reduces digestive problems, and improves nutrition utilization.
7. Feeding Management: Nutrient Supply Optimization
Effective feeding management strategies are required to ensure optimal nutrient intake and utilization. Here are some important considerations:
a) Quality and Quantity of Feed
Choose high-quality feed sources and keep an adequate supply to meet your cattle’s dietary requirements. Regularly evaluate feed quality using laboratory tests and alter rations as needed.
b) Frequency and Consistency of Feeding
To avoid digestive disturbances, keep consistent feeding schedules. Try for consistent feeding intervals to avoid drastic changes in feeding schedules. Feeding consistency promotes healthy rumen function and nutrient absorption.
c) Balanced Rations with Ration Balancing Software for Cattle
A feed formulation or ration balancing software for cattle like FarmSeba can help farmers to determine the nutritional requirements of their cattle.
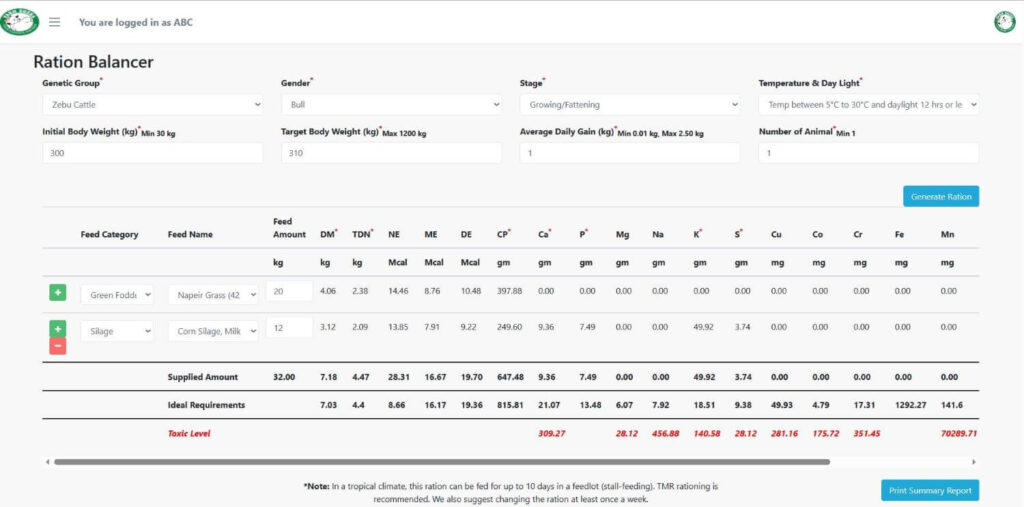
- Accurate Nutrient Analysis: Ration balancing software provides precise and broad nutrient analysis of both feeds and the nutritional requirements of cattle. It considers characteristics such as age, weight, stage of production, and intended performance goals. By entering this data, the software can determine the optimal nutritional quantities required for a balanced diet.
- Feed Optimization: With the help of ration balancing software, cattle farmers can optimize the use of available feed resources. The software considers the nutrient composition of various feed ingredients and helps to calculate or balance the most cost-effective combinations to meet the cattle’s specific nutritional needs. This helps farmers maximize their feed resources while minimizing waste and costs.
- Customized Ration Formulation: Ration balancing software allows cattle farmers to create customized ration formulations according to their herd’s unique requirements. It considers the specific nutrient requirements, feed availability, and any limitations or constraints that need to be taken into account. Farmers can experiment with different scenarios and fine-tune the rations to achieve optimal nutrition and performance.
- Nutrient Gap Analysis: Ration balancing software can detect any deficiencies in nutrition or imbalances in the current diet. It compares the nutrient requirements of the cattle to the nutrient composition of the feed ingredients supplied. The program allows farmers to change the feed and guarantee that the cattle’s nutritional needs are adequately met by indicating any deficiencies.
- Simplified Decision-Making: Ration balancing software simplifies the decision-making process for cattle farmers. It provides clear and concise recommendations based on scientific calculations, reducing the reliance on guesswork and trial-and-error methods. This saves time and allows farmers to make informed decisions regarding feed formulation and management.
Conclusion
Understanding the nutrient requirements of cattle is essential for their health, productivity, and general welfare. You may improve their nutrition and ensure optimal growth and performance by providing the appropriate combination of water, dry matter, energy, protein, vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Remember to follow appropriate feeding management strategies to enhance nutrition supply and to frequently monitor the health of your herd. Your cattle will thrive with sufficient nourishment, and your farming operations will be fruitful.
To Know More
Visit our blog to learn more about FarmSeba and its services. Join us on social media. Write on “FarmSeba Help Desk” for any quarry. To learn how to use FarmSeba, watch video tutorials on our YouTube channel.
